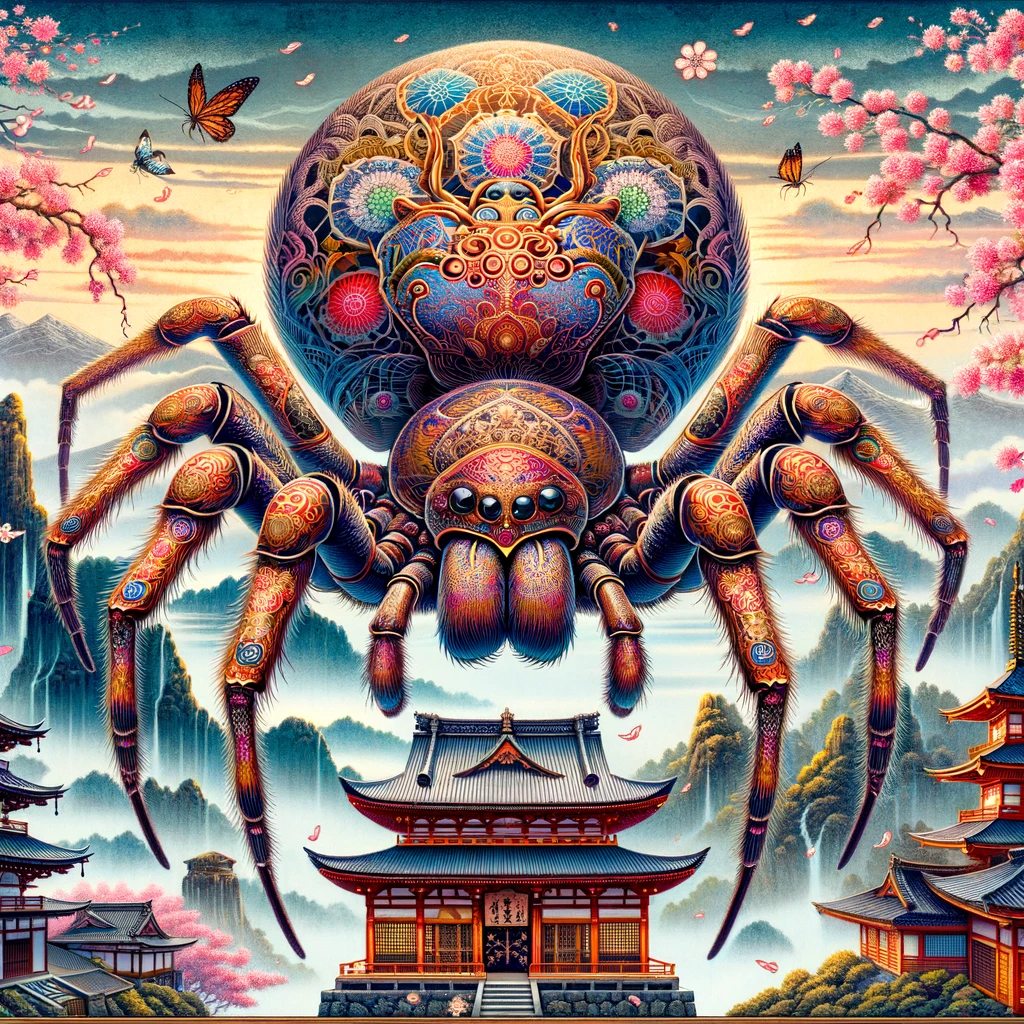
Tsuchigumo, a mysterious and intriguing figure in Japanese folklore, encapsulates the rich tapestry of myth and legend that Japan is known for. This mythical entity, often depicted as a spider, has a deep and complex history, weaving its way through various aspects of Japanese culture.
Origins and Mythology
Tsuchigumo, literally translating to “earth spider,” finds its roots in ancient Japanese folklore and Shinto beliefs. The creature is often portrayed as a yokai (a class of supernatural monsters and spirits) and is sometimes depicted as a spider with supernatural powers and intelligence. The folklore surrounding Tsuchigumo is diverse, with variations in stories and interpretations across different regions of Japan.
Tales and Legends
One of the most famous tales involving Tsuchigumo is from the “Tale of the Heike,” a medieval Japanese epic. In this story, Tsuchigumo is described as a malevolent creature defeated by the heroic Minamoto no Yorimitsu, a famous warrior of the Heian period. According to the legend, Tsuchigumo, disguised as a monk, was confronted by Yorimitsu and his men. Upon being defeated, Tsuchigumo revealed its true form – a gigantic spider.
Another notable story is the legend of Tsuchigumo in the Nara period. Here, the creature is said to have terrorized villagers and was eventually slain by a brave warrior. These tales often depict Tsuchigumo as an antagonist, embodying the fears and uncertainties of the people.
Symbolism and Cultural Impact
In Japanese culture, Tsuchigumo is not just a mythical creature but also a symbol. It often represents manipulation, deceit, and the unknown. The spider’s ability to weave webs is seen metaphorically, symbolizing the complexities of life and the traps one can fall into.
The influence of Tsuchigumo extends to various forms of art and literature. It has been a subject in Noh and Kabuki theater, inspiring plays and performances. Additionally, Tsuchigumo appears in ukiyo-e (woodblock prints) and has been mentioned in several literary works, demonstrating its enduring presence in Japanese culture.
Interpretations and Modern References
Tsuchigumo continues to inspire modern media and entertainment. It appears in manga, anime, and video games, often reinterpreted with contemporary twists. These modern depictions sometimes portray Tsuchigumo in a more sympathetic light, diverging from its traditional villainous image.
Conclusion
The legend of Tsuchigumo is a testament to the enduring power of folklore in shaping cultural identity. This mythical creature, with its deep roots in Japanese history and its ongoing influence in modern culture, serves as a fascinating example of how folklore evolves and adapts over time, retaining its relevance and intrigue in a changing world. Tsuchigumo remains a captivating subject for anyone interested in the rich tapestry of Japanese myth and legend.
